SQL For Data Science: One stop Solution for Beginners
- Why Is SQL Needed For Data Science?
- What Is SQL?
- Basics Of SQL
- Installing MySQL
- Hands-On
Why Is SQL Needed For Data Science?
What Is SQL?
Basics Of SQL
- CREATE DATABASE – creates a brand new database
- CREATE TABLE – creates a new table
- INSERT INTO – inserts new facts into a database
- SELECT – extracts data from a database
- UPDATE – updates information in a database
- DELETE – deletes records from a database
- ALTER DATABASE – modifies a database
- ALTER TABLE – modifies a table
- DROP TABLE – deletes a desk
- CREATE INDEX – creates an index to search an detail
- DROP INDEX – deletes an index
SQL For Data Science – MySQL Demo
1 2 | CREATE DATABASE myfirst;USE myfirst; |
Note:
Step 2: Create a desk with the desired records capabilities
1 | CREATE TABLE toys (TID INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, Item_name TEXT, Price INTEGER, Quantity INTEGER); |
In the above code snippet the following things arise:
- Use the ‘CREATE TABLE’ command to create a table referred to as toys.
- The toy table incorporates four features, particularly, TID (Transaction ID), Item_name, Price and Quantity.
- Each variable is described with their respective statistics sorts.
- The TID variable is said as a number one key. A primary key essentially denotes a variable that could save a unique price.
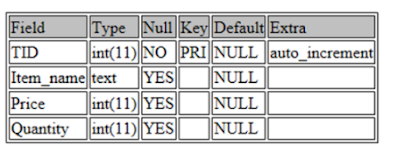
You can in addition check the information of the defined desk via the use of the subsequent command:
1 | DESCRIBE toys; |
Step 3: Inserting data into the table
Now that we’ve created a desk, allow’s fill it up with some values. Earlier on this weblog, I referred to how you could add records into a desk by way of simply the usage of a unmarried command, i.E., INSERT INTO.
Let’s see how that is done:
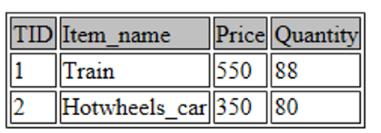
1 2 3 4 5 6 | INSERT INTO toys VALUES (NULL, "Train", 550, 88);INSERT INTO toys VALUES (NULL, "Hotwheels_car", 350, 80);INSERT INTO toys VALUES (NULL, "Magic_Pencil", 70, 100);INSERT INTO toys VALUES (NULL, "Dog_house", 120, 54);INSERT INTO toys VALUES (NULL, "Skateboard", 700, 42);INSERT INTO toys VALUES (NULL, "G.I. Joe", 300, 120); |
In the above code snippet, we definitely inserted 6 observations into our ‘toys’ table by means of the use of the INSERT INTO command. For each commentary, in the brackets, I’ve certain the value of every variable or function that became described while growing the desk.
The TID variable is set to NULL since it auto-increments from 1.
Now allow’s display all of the statistics present in our desk. This can be performed through using the below command:
1 | SELECT * FROM toys; |
Step 4: Modify the statistics entries
Let’s say which you determined to increase the fee of the Ali due to the fact it's miles getting you numerous clients. How might you update the charge of the variable in a database?
It’s easy, simply use the beneath command:
1 | UPDATE toys SET Price=350 WHERE TID=6; |
The UPDATE command permits you to alter any values/variables stored within the desk. The SET parameter allows you to pick a particular characteristic and the WHERE parameter is used to perceive the variable/ cost which you need to alternate. In the above command, I’ve updated the rate of the information entry whose TID is 6 (G.I. Joe).
Now let’s view the updated table:
1 | SELECT * FROM toys; |
You can also adjust what you want to be displayed through just referring to the columns you want to view. For example, the below command will display most effective the name of the toy and its respective charge:
1 | SELECT Item_name, Price FROM toys; |
Step 5: Retrieving statistics
So after putting the facts and modifying it, it’s subsequently time to extract and retrieve the data according to the business necessities. This is in which records may be retrieved for in addition facts analysis and statistics modeling.
Note that may be a simple instance to get you started with SQL, however, in actual-international scenarios the statistics is plenty more complex and big in size. Despite this, the SQL commands nonetheless remain the same and that’s what makes SQL so easy and understandable. It can procedure complicated statistics units with a hard and fast of easy SQL instructions.
Now allow’s retrieve data with a couple of changes. Refer the code below and attempt to apprehend what it does without looking on the output:
1 | SELECT * FROM toys LIMIT 2; |
You guessed it! It displays the first two observations present in my table.
Let’s try something more interesting.
1 | SELECT * FROM toys ORDER BY Price ASC; |
As proven inside the discern, the values are organized with recognize to the ascending order of the fee variable. If you want to search for the 3 most frequently bought objects, what might you do?
It’s quite simple truly!
1 | SELECT * FROM toys ORDER BY Quantity DESC LIMIT 3; |
Let’s try one more.
1 | SELECT * FROM toys WHERE Price > 400 ORDER BY Price ASC; |
This query extracts the details of the toys whose price is more than 400 and arranges the output in ascending order of the price.
So that’s how you can process data by using SQL.















0 Comments